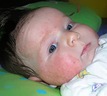
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, refers to an inflammatory disorder of the skin characterized by inflamed skin with a red, rough and an itchy rash. In some cases, the rash may be dry and develop cracks without any eruptions. In some cases, eruptions may arise in the form of papules (small eruptions without any fluid), vesicles (fluid-filled eruptions) or pustules (pus-filled eruptions), or skin peels. The condition may affect a small area or spread all over the body. Itching, with mild or severe intensity, may be felt and skin may bleed on scratching.
Homeopathy provides a very gentle, safe and highly effective treatment option for the cases of eczema. Homeopathic medicines help to reduce skin inflammation by optimizing the overactive immune system and work in restoring the skin barrier to retain skin moisture. Simultaneously, they focus on healing the rash and eruptions on the skin extremely well along with managing attending signs and symptoms like itching, burning, dryness, flaking, tenderness, pain, and bleeding. Further, these remedies halt the progression of the disease and help to treat the root cause that sets in long-term relief rather than temporary comfort. Homeopathy also helps in reducing reliance on harmful topical creams like corticosteroids, hydrocortisone ointments and immune suppressants prescribed in conventional medicine. Medicated creams only remove the outer manifestation of the disease and do not cure eczema. They, rather, harm by driving the disease into some important, centrally-located organ in the body and manifest it in a more harmful way (asthma, for example).
Safe and effective treatment
Homeopathy offers safe and effective treatment for eczema in individuals of all age groups. Homeopathy assures zero side effects of its medicines which are prepared from natural substances.
Homeopathy treats through oral medicines
Homeopathy believes in the principle that skin ailments are an outward expression of some internal disturbance in the body. Therefore, homeopathic medicines focus on healing internally rather than externally (like ointments). These remedies are taken orally (by mouth) that treat the internal turmoil in the body that is being expressed on the skin. Once the internal system attains a state of balance, the symptoms improve gradually.
Individualized approach to treatment
It is the totality of symptoms that help in the correct diagnosis in every individual case and helps in guiding the homeopath to recommend the most suitable homeopathic medicine. In homeopathy, a thorough case-taking is followed by deep evaluation to come to the conclusion regarding the prescription to give the best results. So, one should always take homeopathic medicine for eczema after consulting a qualified homeopathic physician. Self-medication may not help as a person not well acquainted with homeopathic laws does not know how to prescribe the medicines, select the dosage, potency and its repetition.
Homeopathy offers relief without suppression
Homeopathic treatment is non-suppressive, which means that homeopathic remedies do not suppress the symptoms of eczema; they follow an approach to cure it from its origin. If you suppress a disease, there are always chances of some graver manifestation in the body internally. Homeopathic medicines provide natural cure without suppression.
Top 10 Homeopathic Medicines for Eczema
The ten best remedies for the treatment of eczema are Graphites Naturalis, Sulphur, Natrum Muriaticum, Petroleum, Psorinum, Mezereum, Vinca Minor, Tellurium Metallicum, Arsenicum Album and Sepia Officinalis.
1. Graphites Naturalis – Top Grade Medicine for Eczema
Graphites Naturalis is a renowned homeopathic medicine for the cure of eczema. It works wonderfully in case of both, moist eczema and dry eczema. The main signs in dry eczema are excessively rough, dry and unhealthy looking skin accompanied by severe irritation. Cracks may develop on the affected part of the skin.
In moist eczema, it should be used when the skin oozes moist, sticky fluid in any part of the body-bend, such as the elbow, behind the knees, behind the ears, on one’s face (especially around the mouth, chin, and nose), on one’s hands, eyelids, between fingers, and scalp.
When to use Graphites Naturalis?
It is a great choice of medicine for treating both moist and dry eczema. Eczema which is dry with rough skin or cracks as well as moist eczema with discharge of sticky fluid is treated well with the use of Graphites.
How to use Graphites Naturalis?
In a majority cases, it works well in low potencies. To begin with, it can be administered in 3X potency one to two times a day depending on the severity of the complaint.
2. Sulphur – For Eczema with Intense Itching
Sulphur is the best medicine to manage itchy eczema. It can control itching in eczema patches very effectively. Those who need it complain about aggravated itching in the evening and night. Warm temperatures worsen itching which leads to scratching followed by a burning sensation. A person gets relief from itching in the affected part but it appears in some other part of the body. Sulphur can also be used for the symptoms of moist eczema when there is a discharge of yellow fluid from eruptions. Sulphur is also the most appropriate choice of remedy when cases of eczema have been treated with ointments in the past with no relief.
When to use Sulphur?
Sulphur should be administered to treat eczema rashes that have constant itching and aggravate in the evening and night.
How to use Sulphur?
Though it can be used in both low and high potencies, it is safe to ingest 30C power initially. Its dosage should not exceed one dose daily. Do not use its high potencies without a homeopath’s consultation.
3. Natrum Muriaticum – For Eczema On The Margins Of The Hairline
For eczema on the edges of the hair, Natrum Muriaticum is a highly recommended medicine. There is marked redness and inflammation on the edge of the hairline. The rash may ooze fluid. It may also damage the hair. Dry, red and inflamed rashes in eczema are wonderfully treated by using this medicine.
When to use Natrum Muriaticum?
This medicine can be administered if eczema is specifically located on the margins of the hairline with excessive inflammation and redness.
How to use Natrum Muriaticum?
Natrum Mur 6X can be administered twice or thrice daily as per the intensity of the complaint.
4. Petroleum – For Eczema With Deep Cracks And Bleeding
The key symptom to use petroleum in eczema is when you see deep cracks on the skin, accompanied by bleeding. Where eczema hits, the skin gets hard, dry, and rough. This medicine helps reduce the dryness of skin and heals the cracks most gently and effectively. Although cracks can develop on the skin in any part of the body, hands are the most affected which may feel itching and burning sensation. In several cases, eczema tends to worsen in the winters, for which petroleum is the most prescribed remedy.
When to use Petroleum?
Petroleum should be used if eczema is accompanied by bleeding and deep cracks. It is also one of the best homeopathic remedies to soothe flare-ups of eczema in the winters.
How to use Petroleum?
It can be administered in 30C potency two times a day for best possible results.
5. Psorinum – For Eczema In Bends (Folds Of Skin)
Psorinum is a very effective medicine when eczema appears in the bends or the folds of the skin. Rashes may appear on the bends of the elbow, armpit-folds or area behind the ear. In case of eczema behind the ear, a discharge may ooze; the rash may be itchy which disturb one’s sleep. Another key symptom to use this medicine is intolerable itching and crusty eruptions.
When to use Psorinum?
This medicine is recommended when eczema appears on the bends/folds of skin like elbow, armpits accompanied by severe itching and dryness.
How to use Psorinum?
It is advised to use Psorinum in 200C potency and even potencies higher than this. Don’t use this medicine without the advice of a homeopath since it is a strong medicine and the dose may vary on a case-to-case basis and is usually not to be repeated frequently.
6. Mezereum – For Thick, Crusty Eruptions With Pus Underneath
Mezereum is an important medicine to manage cases of eczema with thick crusty eruptions along with the presence of pus underneath. It is accompanied by intolerable itching. At times, the eruptions may bleed upon being touched. It is also administered in case of eczema on scalp gluing/sticking of hair.
When to use Mezereum?
The characteristic feature for the use of this medicine in eczema is eruptions covered with thick crusts and pus collection beneath the skin.
How to use Mezereum?
This medicine is mostly administered in 30 C potency once daily. To use higher potencies like 200C seek a qualified homeopath’s advice.
7. Vinca Minor – For Eczema Of Scalp With Sticky And Foul Discharge
Vinca Minor is a natural remedy prepared from plant “Lesser Periwinkle”. It is mostly administered in cases of eczema of the face and scalp, especially in children. Eruptions are accompanied by thick, sticky, offensive, purulent or honey-like discharge that causes formation of thick crusts due to which hair becomes matted and glued together due to exudation. Severe itching that worsens from scratching is also a leading symptom to administer this medicine. Eczema is associated with impetigo-like eruptions. Skin appears unhealthy, with a tendency to ulceration under crusts.
When to use Vinca Minor?
Vinca minor is particularly of use in pediatric scalp eczema where offensive exudation and thick crust formation are key symptoms.
How to use Vinca Minor?
Vinca minor 30C can be administered twice or thrice daily for best possible results.
8. Tellurium Metallicum – For Ring-Shaped, Offensive Eczema
Tellurium Metallicum is one of the best medicines for ring-shaped (circular) eczematous eruptions with clearly defined margins. Eczema spreading in concentric circles that is often mistaken for ringworm is treated with this medicine. Severe itching and burning sensation is an accompanying factor, especially at night. Eczema commonly affects face, ears, hands, and extremities. Eruptions tend to spread from the center to the periphery, leaving central clearing. Skin may be sensitive and painful after scratching.
When to use Tellurium Metallicum?
Tellurium is a key remedy for those cases of eczema where it presents in annular (circular) patterns with offensive discharge and marked itching, especially when the eruption spreads peripherally.
How to use Tellurium Metallicum?
It is safe to administer this medicine in 30C potency initially, once to thrice a day but for high potencies like 200 C or more, consultation with a homeopathic physician is strictly recommended.
9. Arsenicum Album – For Eczema with Burning Pains Relieved By Warmth
Arsenicum Album is administered in both moist and dry eczema with severe burning pain, often relieved by warmth. Restlessness and anxiety accompanies skin complaints and the patients cannot keep still. Thin, watery, acrid discharge from the eruptions excoriates the surrounding skin. The skin appears scaly, dry, rough, or cracked; and it may alternate with oozing. The eczema worsens due to cold, cold air, damp weather. Marked weakness and exhaustion disproportionate to skin lesions is a key factor to use arsenicum album. Chronic, relapsing eczema with unhealthy skin is treated with this medicine in a very effective manner.
When to use Arsenicum Album?
Arsenicum Album is especially administered when burning and anxiety dominates the case, and the patient feels better with heat, despite the skin appearing inflamed or excoriated.
How to use Arsenicum Album?
It is safe to use it in 30C potency to begin with, once to thrice a day but for high potencies like 200 C or more, consultation with a homeopathic physician is strictly advised.
10. Sepia Officinalis – For Eczema Getting Worse from Warmth with Marked Intolerance to Heat
Sepia Officinalis is a very effective medicine for scaly, dry, or slightly moist eczema with marked itching and burning. Eczema with brownish or yellowish discoloration of the skin that mainly occurs in skin folds – behind ears, on the elbow and knee bends, and groins. It is indicated in chronic eczemas with tendency to cracking and soreness. Itching worsens due to warmth of bed and sweating. Skin complaints are usually associated with hormonal imbalance, especially in women and patients often present with mental indifference, fatigue and irritability.
When to use Sepia Officinalis?
Sepia is particularly useful in chronic, relapsing eczema, especially among women, where symptoms aggravate due to heat and sweating and improves in fresh and cool air.
How to use Sepia Officinalis?
It is safe to administer it in 30C potency in the beginning, one to three times a day but for high potencies like 200 C or more, consultation with a homeopath is strictly advised.
Note: One may consider using these medicines for about two-three weeks. To prolong their use and switching to high potencies, consultation with a homeopath is a must.
What causes Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a major role in its development. Those with a family history of eczema or any other allergy (over-reaction of the immune system to something that does not have any effect on the majority of people) such as nasal allergy, asthma, etc are at a higher risk of developing eczema. According to research, those suffering from eczema do not produce adequate protein filaggrin, which is responsible for keeping skin moisturised, healthy and maintaining the skin barrier.
There are a few environmental triggers that can flare up eczema. These include irritants (like soaps, and detergents), certain food items (like dairy products, eggs, nuts, and wheat), extreme temperatures (either extreme hot or extreme cold), low humidity (dry air), increased sweating, allergens (e.g. dust mites, pet dander), synthetic fabric, wool, and stress.
What are the various types of Eczema?
Various types of eczema include seborrhoeic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and venous/stasis eczema.
1. Atopic dermatitis
Characterised by skin inflammation there is a presence of dry, itchy rash. This disease runs in the family and its onset happens during childhood. Atopy refers to a genetic tendency to develop allergic diseases. Asthma and hay fever are often reported in addition to eczema in atopic dermatitis. The signs and symptoms vary as per the age group. In kids up to two years of age, the rash mainly appears on the scalp and face, especially on the cheeks. In 3-18 years of age, rashes occur frequently on the bends of the elbow or knees, ankle, wrist, or neck. In adults, the rash mainly is seen on the bends of the elbow, neck and knee, and sometimes may cover the entire body.
2. Contact dermatitis
It is mainly of two types –irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
1. In allergic contact dermatitis, the allergic reaction appears on the skin when exposed to a foreign substance, like metals (nickel, gold) or cosmetics.
2. Irritant contact dermatitis arises when the skin comes in contact with a toxic or irritant substance, such as detergent, bleach, or battery acid.
3. Seborrhoeic dermatitis
It mainly affects the face, scalp, and eyelids and shows up as flakes or as greasy/ crusty eruptions. Among the infants, thick, crusty eruptions appear on the scalp that are referred to as cradle caps.
4. Dyshidrotic eczema
It is mainly visible on the palms and the soles. It is characterized by the presence of vesicles (fluid-filled bumps)
5. Venous/ stasis eczema
It mainly develops on the lower limbs due to poor blood circulation and varicose veins. One is susceptible to develop leg ulcers in such cases.
How to diagnose eczema?
A physician can easily diagnose a case of eczema by looking at the skin eruptions/rash and reviewing its accompanying symptoms and the medical history of the patient. A family history of eczema adds to the likelihood of its presence. There are no specific lab investigations required for eczema diagnosis. However, in some cases, a doctor may recommend tests to examine if there is skin allergy. It includes a patch test to find out specific allergens that might be the trigger point for the symptoms. In this test a few allergens after being put on a patch are applied to the skin. In case any of these allergens are triggering the complaint, that area will become inflamed.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. At what age is eczema likely to appear?
In a majority of the cases, eczema starts early, sometimes before five years of age. However, eczema can show up among the teenagers and also among adults.
2. Which part of the skin is more vulnerable to eczema?
Eczema may develop anywhere on the skin from head to toe but may vary with the age group. Among the children, common areas are the scalp, face, and chest. Adults are more likely to get eczema on the elbow bends and behind the knees.
3. Why does my child have eczema?
The answer could lie in his genes. If a child has eczema, there is a chance he has atopic dermatitis. Atopy is a term applied to a genetic predisposition toward developing allergic diseases like dermatitis, hay fever, and asthma. But, there are chances that your child’s eczema disappear as he gets older. However, the age at which a child will start to show improvement varies though most children start getting better by the age of three years.
4. Is eczema an allergy?
There are cases of eczema that are allergic in origin, but not every case is an allergy. In allergic eczema, the skin reacts after coming in contact with an allergen. A few common allergens are poison ivy (a plant), cosmetics, nickel, and antibiotic creams.
5. Can eczema spread from skin contact?
No, eczema is not contagious at all. It does not spread from one person to another via the skin.
6. Is eczema related to weather?
Eczema can occur irrespective of the weather conditions though it usually is activated by the cold weather.
7. Why does eczema keep coming back?
Relapse of eczema happens due to stress, dust, weather changes, sweating, soaps, or certain types of foods.
8. What daily care can help in managing eczema?
Daily skin care routine like regular moisturizing, avoiding harsh soaps, keeping skin clean and dry and most importantly identifying and avoiding triggers can help manage eczema better.
9. How long does eczema take to improve?
Improvement depends on intensity, duration, triggers, and regular treatment. Chronic cases need patience.
10. Can stress worsen eczema?
Yes. Emotional stress is a common trigger that can worsen itching and flare-ups.
11. Is bathing harmful in eczema?
No. Gentle, quick baths with lukewarm water are helpful if followed by moisturising.
12. Can eczema cause skin darkening or marks?
Yes. Repeated swollenness and scratching can cause dark patches or thickened of the skin, but it mostly gets better as one heals.